EHEDG White Paper GFSI now available

Now available for all
EHEDG White Paper on GFSI Hygienic Design JI & JII
GFSI paves the way to incorporate hygienic design in food safety management programmes. But what practical implications can be expected for food processing companies and their equipment suppliers? This document aims to offer support to all the farm-to-fork chain stakeholders in interpreting and applying the requirements of scopes JI/JII. Reference is given to relevant literature.
EHEDG White Paper on GFSI Hygienic Design Scopes JI & JII
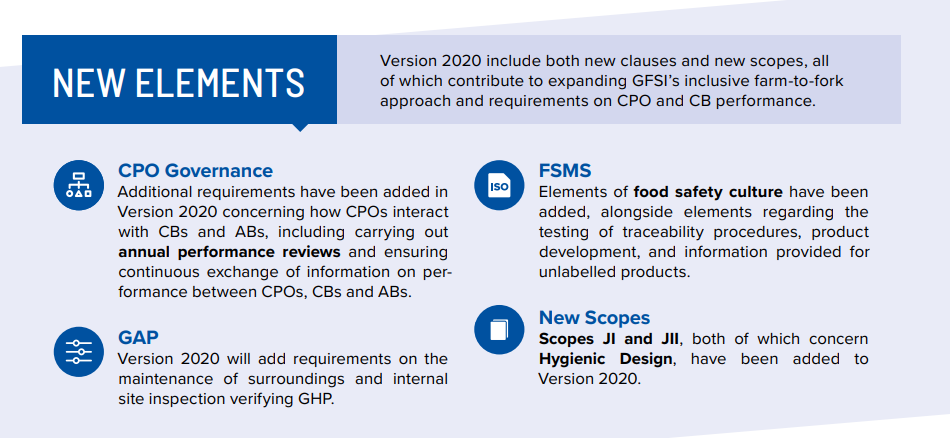
In 2020 the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) published a high-level set of hygienic design benchmarking requirements with the objective of enhancing food safety from farm to fork. These Hygienic Design of Food Buildings and Processing Equipment requirements were published as scope JI (for building constructors and equipment manufacturers) and scope JII (for building and equipment users).
(source: mygfsi.com)
Certification Programme Owners (CPOs) will include the benchmarking requirements of scopes JI and JII in their standards for GFSI-recognised certification of the hygienic design, fabrication, installation, maintenance and cleanability of facilities and equipment. Compliance with these standards will benefit supply chain stakeholders and consumers by contributing to consistent food safety and quality across the global food supply chain.
3-A Sanitary Standards Inc. (3-A SSI) and the European Hygienic Engineering and Design Group (EHEDG) have a long history of developing criteria for the hygienic design of buildings and equipment in the form of standards and guidelines. These are essential tools for equipment manufacturers, building constructors and food manufacturers to meet food safety and quality objectives and for government agencies and regulatory authorities to achieve public health objectives.
Together, 3-A SSI and EHEDG welcome this GFSI initiative. With the recently launched EHEDG White Paper on GFSI Hygienic Design Scopes JI & JII, the EHEDG organisation would like to provide support to its stakeholders in the farm-to-fork chain, in interpreting and applying the requirements of scopes JI and JII.
This white paper is not a standard, it presents the EHEDG views on the GFSI benchmarking requirements and advice and recommendations on how these can be fulfilled. It gives guidance to EHEDG stakeholders, and is not aimed to provide any views regarding the GFSI organisation or any other organisation involved in composing the benchmarking requirements.
All EHEDG company and institute members can download it after log-in here.
Objective and Scope
Anticipating the inclusion of the GFSI hygienic design benchmarking requirements by Certification Programme Owners, EHEDG has compiled this white paper to give guidance to companies that are interested in applying the requirements of GFSI scope JI or JII. Ultimately it will be the CPO standards, based on GFSI scope JI or JII requirements, against which companies can be certified.
JI for food building constructors and processing equipment manufacturers, including, according to the GFSI, the following product services and activities:
Manufacturers of equipment, including any components necessary to link them together, and their utilities and utensils necessary for their operation, for farms, food production facilities, food retail and wholesale operations, and packaging dedicated to food;
Architects, Engineers and Designers of food handling facilities, including farm, food manufacturing, storage and retail buildings;
The builders of the above facilities.
JII for food building and processing equipment users, including, according to the GFSI, the following product services and activities
Specifying, purchasing, design and construction of buildings or refurbishments by farmers, food manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers, and packaging manufacturers for their own use;
Specifying, purchasing, design and construction of equipment, including any components necessary to link them together, and their utilities and utensils necessary for their operation, and facilities by farmers, food manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers, and packaging manufacturers for their own use.
The structure of this white paper follows the structure of the GFSI benchmarking requirement documents JI and JII. For each requirement, interpretations, guidance and references (recognised standards and EHEDG guidelines) are given.
JI for building constructors and equipment manufacturers, covers the requirements for the establishment of a Hygienic Design Management System including hygienic design, hazard and risk management and good industry practice requirements.
JII for building and equipment users, can be seen as hygienic design requirements additional to the scope of recognition that the building and equipment users will already comply to. It is about integrating hygienic design into existing Food Safety Management Systems.
The method of executing food safety management may differ between the users of JI and JII:
Food manufacturers are typically familiar with HACCP or HACCP-based concepts as part of their Food Safety Management System (reference ISO 22000:2021) of which hygienic design is a prerequisite programme, whereas equipment manufacturers are typically familiar with hygiene risk assessments based on EN 1672-2:2020, ISO 14159:2008, or other recognised standards. It is important for food-safety management that expectations and interpretations of needs, capabilities and intended use are clear during development, realisation or handover of food buildings and equipment.
Sections and associated elements that require reference to EHEDG guidelines
Section 1: Hazard and Risk Management Systems Requirements (HACCP)
Hygienic design process; Risk assessment; Intended use of the building or equipment; Hygienic design principles
EHEDG Guideline 8: Hygienic design principles (2018)
EHEDG Guideline 9: Welding stainless steel to meet hygienic requirements (1993)
EHEDG Guideline 10: Hygienic design of closed equipment for the processing of liquid food (2007)
EHEDG Guideline 13: Hygienic design of equipment for open processing (2004)
EHEDG Guideline 22: General hygienic design criteria for the safe processing of dry particulate materials (2014)
EHEDG Guideline 23: Use of H1 and HT1 registered lubricants Part 1 and production of H1 & HT1 food grade registered lubricants, Part 2 (2018)
EHEDG Guideline 28: Safe and hygienic treatment, storage and distribution of water in food and beverage factories (2018)
EHEDG Guideline 32: Materials of construction for equipment in contact with food (2005)
EHEDG Guideline 34: Integrating hygienic entities (2020)
EHEDG Guideline 36: Hygienic welding of stainless steel tubing in the food processing Industry (2006)
EHEDG Guideline 44: Hygienic design principles for food factories (2014)
EHEDG Guideline 45: Cleaning validation, monitoring and Vverification (2021)
EHEDG Guideline 50: Hygienic design requirements for CIP Installations (2019)
EHEDG Guideline 52: Basic principles of cleaning and disinfection in food manufacturing (2021)
EHEDG Guideline 54: Testing of hygienic weld joints (2020)
EHEDG Guideline 58: Hygienic design risk management (expected: 2023)
Section 2: Food Safety (or Hygienic Design) Management Systems Requirements (FSM)
Purchasing and supplier performance; Product release
EHEDG Guideline 34: Integrating hygienic entities (2020)
EHEDG Guideline 44: Hygienic design principles for food factories (2014)
EHEDG Guideline 58: Hygienic design risk management (expected: 2023)
Section 3: Good Industry (Sector) Practice Requirements (GMP)
Equipment; Product contamination risk and segregation; Training
EHEDG Guideline 8: Hygienic design principles (2018)
EHEDG Guideline 18: Chemical treatments of stainless steel Surfaces (2014)
EHEDG Guideline 34: Integrating hygienic entities (2020)
EHEDG Guideline 44: Hygienic design principles for food factories (2014)
EHEDG Guideline 47: Air handling systems in the food industry - Air quality control for building ventilation (2016)
EHEDG Guideline 45: Cleaning validation, monitoring and verification (2021)
EHEDG Guideline 52: Basic principles of cleaning and disinfection in food manufacturing (2021)
EHEDG Guideline 58: Hygienic design risk management (expected: 2023)
Watch the interview with Patrick Wouters, Global Hygienic Design Lead at Cargill, EHEDG Vice-President and Chair of the Hygienic Design Benchmarking Support Group
Watch the interview with John Holah (EHEDG Hygienic Design Benchmarking Support Group)
Watch the interview with former QA Manager Unilever, Kraftfoods International & METRO AG Peter Overbosch (EHEDG Hygienic Design Benchmarking Support Group)










